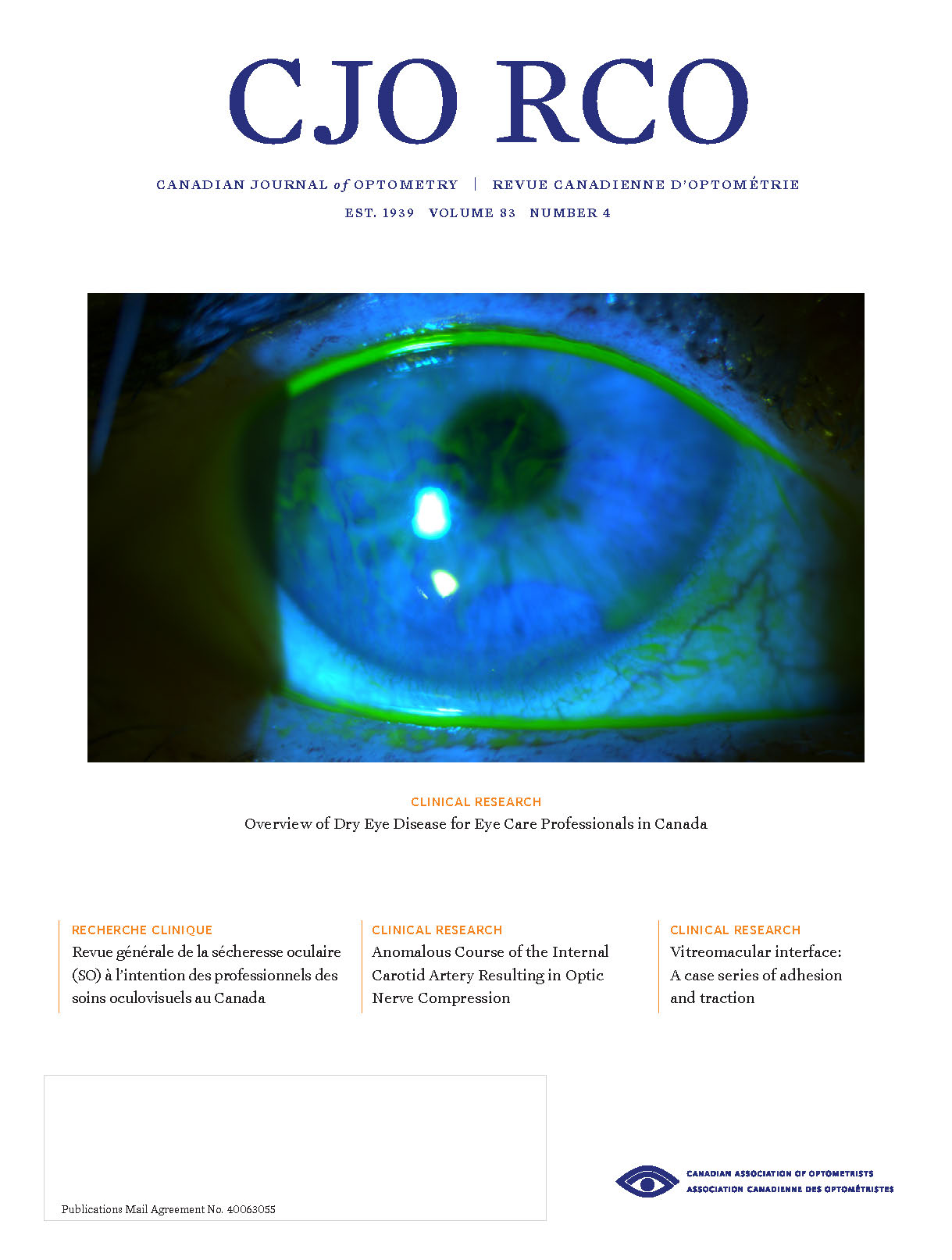
Anomalous Course of the Internal Carotid Artery Resulting in Optic Nerve Compression
DOI:
https://doi.org/10.15353/cjo.v83i4.1795Keywords:
optic neuropathy, internal carotid artery, optical coherence tomography, Humphrey visual field, magnetic resonance imagingAbstract
Compression of the optic nerve by the internal carotid artery can occur due to their proximity as they exit the cavernous sinus. This report details a case of unilateral compressive optic neuropathy resulting from an anomalous course of the internal carotid artery. It presents optical coherence tomography scans, Humphrey visual field results, and magnetic resonance images, as well as reviews other causes of optic neuropathy that can have a similar clinical presentation.
Published
2021-11-24
How to Cite
Vance Taylor, D., Cappelli, R., & Wiedemann, L. (2021). Anomalous Course of the Internal Carotid Artery Resulting in Optic Nerve Compression. Canadian Journal of Optometry, 83(4), 39–44. https://doi.org/10.15353/cjo.v83i4.1795
Issue
Section
Original Research
License
Copyright (c) 2021 Danielle Vance Taylor, OD, Rena Cappelli, OD, MPH, FAAO, Leah Wiedemann, OD, FAAO

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-NoDerivatives 4.0 International License.